Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Mn
MnShimizu, Kazuyuki*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Tsuru, Tomohito; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 245, p.116051_1 - 116051_6, 2024/05
Hydrogen at the mass ppm level causes hydrogen embrittlement in metallic materials, but it is extremely difficult to experimentally elucidate the hydrogen trapping sites. We have taken advantage of the fact that positive muons can act as light isotopes of hydrogen to study the trapping state of hydrogen in matter. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments and the density functional theory (DFT) calculations for hydrogen trapping energy are carried out for Al Mn. The DFT calculations for hydrogen in Al
Mn. The DFT calculations for hydrogen in Al Mn have found four possible trapping sites in which the hydrogen trapping energies are 0.168 (site 1), 0.312 (site 2), 0.364 (site 3), and 0.495 (site 4) in the unit of eV/atom. Temperature variations of the deduced dipole field width (
Mn have found four possible trapping sites in which the hydrogen trapping energies are 0.168 (site 1), 0.312 (site 2), 0.364 (site 3), and 0.495 (site 4) in the unit of eV/atom. Temperature variations of the deduced dipole field width ( ) indicated step-like changes at temperatures, 94, 193, and 236 K. Considering their site densities, the observed
) indicated step-like changes at temperatures, 94, 193, and 236 K. Considering their site densities, the observed  change temperatures are interpreted by trapping muons at sites 1, 3, and 4.
change temperatures are interpreted by trapping muons at sites 1, 3, and 4.
Tang, J.*; Wang, Y.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 239, p.115804_1 - 115804_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behaviors induced by the combination of external and internal hydrogen (H) in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy were systematically investigated via in situ 3D characterization techniques. SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy could initiate and propagate in the potential crack region where the H concentration exceeded a critical value, in which the nanoscopic H-induced decohesion of  -MgZn
-MgZn precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Materialia, 32, p.101934_1 - 101934_12, 2023/12
Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Materialia, 32, p.101943_1 - 101943_8, 2023/12
Dannoshita, Hiroyuki*; Hasegawa, Hiroshi*; Higuchi, Sho*; Matsuda, Hiroshi*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Umezawa, Osamu*
Scripta Materialia, 236, p.115648_1 - 115648_5, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining
ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysis
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysisMao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Scripta Materialia, 235, p.115642_1 - 115642_6, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)In the present study, a hybrid  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation measurement was performed on tensile deformation of an ultrafine grain (UFG) stainless steel exhibiting a huge L
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation measurement was performed on tensile deformation of an ultrafine grain (UFG) stainless steel exhibiting a huge L ders band deformation to evaluate the individual contribution of the austenite matrix and the deformation-induced martensite to the strain hardening during the propagation of the band. Quantitative analysis revealed that the strain hardening of the austenite matrix was insufficient to maintain a uniform deformation when the flow stress was greatly enhanced by the UFG structure. The strain hardening required for the L
ders band deformation to evaluate the individual contribution of the austenite matrix and the deformation-induced martensite to the strain hardening during the propagation of the band. Quantitative analysis revealed that the strain hardening of the austenite matrix was insufficient to maintain a uniform deformation when the flow stress was greatly enhanced by the UFG structure. The strain hardening required for the L ders band to propagate was mostly provided by the formation of martensite and the high internal stress within it.
ders band to propagate was mostly provided by the formation of martensite and the high internal stress within it.
 titanium alloys strong and ductile
titanium alloys strong and ductileChong, Y.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; Guo, B.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Zhao, G.*; Yoshida, Shuhei*; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Godfrey, A.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 257, p.119165_1 - 119165_14, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:84.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastable  titanium alloys possess excellent strain-hardening capability, but suffer from a low yield strength. As a result, numerous attempts have been made to strengthen this important structural material in the last decade. Here, we explore the contributions of grain refinement and interstitial additions in raising the yield strength of a Ti-12Mo (wt.%) metastable
titanium alloys possess excellent strain-hardening capability, but suffer from a low yield strength. As a result, numerous attempts have been made to strengthen this important structural material in the last decade. Here, we explore the contributions of grain refinement and interstitial additions in raising the yield strength of a Ti-12Mo (wt.%) metastable  titanium alloy. Surprisingly, rather than strengthening the material, grain refinement actually lowers the ultimate tensile strength in this alloy. This unexpected and anomalous behavior is attributed to a significant enhancement in strain-induced
titanium alloy. Surprisingly, rather than strengthening the material, grain refinement actually lowers the ultimate tensile strength in this alloy. This unexpected and anomalous behavior is attributed to a significant enhancement in strain-induced  martensite phase transformation, where in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis reveals, for the first time, that this phase is much softer than the parent
martensite phase transformation, where in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis reveals, for the first time, that this phase is much softer than the parent  phase. Instead, a combination of both oxygen addition and grain refinement is found to realize an unprecedented strength-ductility synergy in a Ti-12Mo-0.3O (wt.%) alloy. The advantageous effect of oxygen solutes in this ternary alloy is twofold. Firstly, solute oxygen largely suppresses strain-induced transformation to the
phase. Instead, a combination of both oxygen addition and grain refinement is found to realize an unprecedented strength-ductility synergy in a Ti-12Mo-0.3O (wt.%) alloy. The advantageous effect of oxygen solutes in this ternary alloy is twofold. Firstly, solute oxygen largely suppresses strain-induced transformation to the  martensite phase, even in a fine-grained microstructure, thus avoiding the softening effect of excessive amounts of
martensite phase, even in a fine-grained microstructure, thus avoiding the softening effect of excessive amounts of  martensite. Secondly, oxygen solutes readily segregate to twin boundaries, as revealed by atom probe tomography. This restricts the growth of
martensite. Secondly, oxygen solutes readily segregate to twin boundaries, as revealed by atom probe tomography. This restricts the growth of 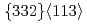 deformation twins, thereby promoting more extensive twin nucleation, leading to enhanced microstructural refinement. The insights from our work provide a cost-effective rationale for the design of strong yet tough metastable
deformation twins, thereby promoting more extensive twin nucleation, leading to enhanced microstructural refinement. The insights from our work provide a cost-effective rationale for the design of strong yet tough metastable  titanium alloys, with significant implications for more widespread use of this high strength-to-weight structural material.
titanium alloys, with significant implications for more widespread use of this high strength-to-weight structural material.
Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Bai, Y.*; Harjo, S.; Park, M.-H.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 256, p.119139_1 - 119139_16, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:90.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP)-assisted steels exhibit an excellent combination of strength and ductility due to enhanced strain hardening rate associated with deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT). Quantitative evaluation on the role of DIMT in strain hardening behavior of TRIP-assisted steels and alloys can provide guidance for designing advanced materials with strength and ductility synergy, which is, however, difficult since the phase composition keeps changing and both stress and plastic strain are dynamically partitioned among constituent phases during deformation. In the present study, tensile deformation with  neutron diffraction measurement was performed on an Fe-24Ni-0.3C (wt.%) TRIP-assisted austenitic steel. The analysis method based on stress partitioning and phase fractions measured by neutron diffraction was proposed, by which the tensile flow stress and the strain hardening rate of the specimen were resolved into factors associated with each phase, i.e., the austenite matrix, deformation-induced martensite, and the transformation rate of DIMT after differentiation, and then the role of each factor in the global strain hardening behavior was discussed. In addition, the plastic strain partitioning between austenite and martensite was indirectly estimated using the dislocation density measured by diffraction profile analysis, which constructed the full picture of stress and strain partitioning between austenite and martensite in the material. The results suggested that both the transformation rate and the phase stress borne by the deformation-induced martensite played important roles in the global tensile properties of the material. The proposed decomposition analysis method could be widely applied to investigating mechanical behavior of multi-phase alloys exhibiting the TRIP phenomenon.
neutron diffraction measurement was performed on an Fe-24Ni-0.3C (wt.%) TRIP-assisted austenitic steel. The analysis method based on stress partitioning and phase fractions measured by neutron diffraction was proposed, by which the tensile flow stress and the strain hardening rate of the specimen were resolved into factors associated with each phase, i.e., the austenite matrix, deformation-induced martensite, and the transformation rate of DIMT after differentiation, and then the role of each factor in the global strain hardening behavior was discussed. In addition, the plastic strain partitioning between austenite and martensite was indirectly estimated using the dislocation density measured by diffraction profile analysis, which constructed the full picture of stress and strain partitioning between austenite and martensite in the material. The results suggested that both the transformation rate and the phase stress borne by the deformation-induced martensite played important roles in the global tensile properties of the material. The proposed decomposition analysis method could be widely applied to investigating mechanical behavior of multi-phase alloys exhibiting the TRIP phenomenon.
 Mg and long-period stacking ordered phases in a Mg-Zn-Y alloy by hot-extrusion with low extrusion ratio
Mg and long-period stacking ordered phases in a Mg-Zn-Y alloy by hot-extrusion with low extrusion ratioHarjo, S.; Gong, W.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kawasaki, Takuro; Yamasaki, Michiaki*
Acta Materialia, 255, p.119029_1 - 119029_12, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:95.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionGong, W.; Harjo, S.; Tomota, Yo*; Morooka, Satoshi; Kawasaki, Takuro; Shibata, Akinobu*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 250, p.118860_1 - 118860_16, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.65(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kwon, H.*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Kimizuka, Hajime*; Oda, Takuji*
Acta Materialia, 247, p.118739_1 - 118739_11, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:74.65(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We estimate the diffusivity of dilute hydrogen in body-centered-cubic metals, Nb, Fe, and W, from path integral simulations using machine-learning moment tensor potentials with an accuracy level of density functional theory. Our computational results show great agreement with some experimental results that appear to be accurate. The isotope effects are also reproduced consistently with the experimental data.
Kwon, H.*; Sathiyamoorthi, P.*; Gangaraju, M. K.*; Zargaran, A.*; Wang, J.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Lee, B.-J.*; Kim, H. S.*
Acta Materialia, 248, p.118810_1 - 118810_12, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:99.28(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Woo, W.*; Kim, Y. S.*; Chae, H. B.*; Lee, S. Y.*; Jeong, J. S.*; Lee, C. M.*; Won, J. W.*; Na, Y. S.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; et al.
Acta Materialia, 246, p.118699_1 - 118699_13, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:98.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Wang, Y.*; Tomota, Yo*; Omura, Takahito*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.
Materialia, 27, p.101685_1 - 101685_9, 2023/03
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyGong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Zheng, R.*; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Sun, B.*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Harjo, S.; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Scripta Materialia, 225, p.115161_1 - 115161_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.58(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Lam, T.-N.*; Chin, H.-H.*; Zhang, X.*; Feng, R.*; Wang, H.*; Chiang, C.-Y.*; Lee, S. Y.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Liaw, P. K.*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 245, p.118585_1 - 118585_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:80.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionSawaguchi, Takahiro*; Tomota, Yo*; Yoshinaka, Fumiyoshi*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118494_1 - 118494_14, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) phase to
phase to  phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformation
phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformationGuo, B.*; Mao, W.; Chong, Y.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, H.*; Jonas, J. J.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118427_1 - 118427_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:64.46(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tsuchida, Noriyuki*; Ueji, Rintaro*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.
Scripta Materialia, 222, p.115002_1 - 115002_6, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:64.46(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Chong, Y.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Guo, B.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; Inoue, Koji*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 240, p.118356_1 - 118356_15, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:92.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we systematically investigated the influences of nitrogen content and grain size on the tensile properties and deformation behaviors of titanium at room temperature. By high-pressure torsion and annealing, we obtained ultrafine-grained (UFG) Ti-0.3wt.%N alloy with a fully recrystallized microstructure, which combined an unprecedented synergy of ultrahigh yield strength (1.04 GPa) and large uniform elongation (10%). The hardening and strain-hardening mechanisms of Ti-0.3wt.%N alloy were comprehensively studied via deformation substructure observation and first-principles calculations. It is revealed that the contributions of nitrogen to the excellent strength/ductility balance in UFG Ti-0.3wt.%N were twofold. On one hand, nitrogen atoms inside the grains strongly impeded the motion of 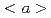 dislocations on prismatic plane due the shuffling of nitrogen from octahedral to hexahedral site, giving rise to a six-fold increase in the friction stress than pure Ti. Moreover, the greatly reduced stacking fault energy difference between prismatic and pyramidal planes in Ti-0.3wt.%N alloy facilitated an easier activation of
dislocations on prismatic plane due the shuffling of nitrogen from octahedral to hexahedral site, giving rise to a six-fold increase in the friction stress than pure Ti. Moreover, the greatly reduced stacking fault energy difference between prismatic and pyramidal planes in Ti-0.3wt.%N alloy facilitated an easier activation of 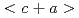 dislocations, which contributed to an enhanced strain-hardening rate. On the other hand, some nitrogen atoms segregated near the grain boundaries, a phenomenon discovered in
dislocations, which contributed to an enhanced strain-hardening rate. On the other hand, some nitrogen atoms segregated near the grain boundaries, a phenomenon discovered in  -titanium for the first time. These segregated nitrogen atoms served as an additional contributor to the yield strength of UFG Ti-0.3wt.%N, by raising the barrier against dislocation slip transfer between grains. Our experimental and theoretical calculation work provide insights for the design of affordable high strength titanium without a large sacrifice of ductility, shedding lights on a more widespread use of this high strength to weight material.
-titanium for the first time. These segregated nitrogen atoms served as an additional contributor to the yield strength of UFG Ti-0.3wt.%N, by raising the barrier against dislocation slip transfer between grains. Our experimental and theoretical calculation work provide insights for the design of affordable high strength titanium without a large sacrifice of ductility, shedding lights on a more widespread use of this high strength to weight material.